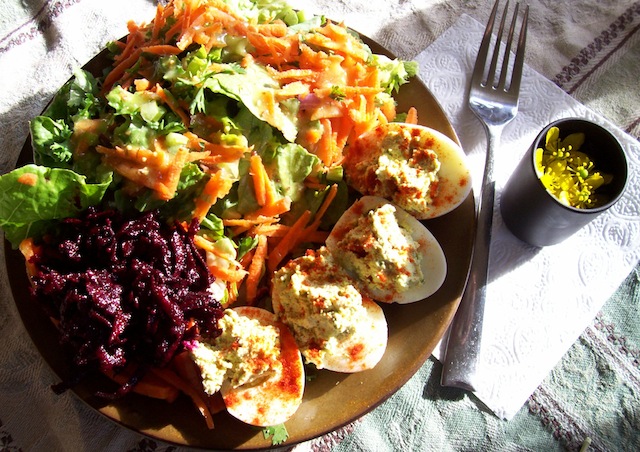
Here is a light lunch of deviled eggs with salad and grated beets. Eggs are one of the cheapest and easiest foods to prepare. Just ensure you have a quality source for your eggs.
During the last few weeks, I have had a number of conversations from overwhelmed newcomers to nourishing traditional foods. “What is the best way to save money on nourishing traditional foods? How can I find time to make nourishing meals for my family when I am so busy? Do I need to take supplements?” These are examples of the typical questions. I hope the following posting will help people making the transition to nourishing traditional foods. Remember, you do not have to do it alone. There is a whole community with a vast store of knowledge willing to help.
So, how do you start if you have limited time and a limited budget? The Big Changes will take some planning and organizing on a seasonal basis. These changes are more expensive in the short term but will save a lot money over a year. The Little Changes can be done in the household and require only weekly planning and a regular program of self-education. There is no reason to rush. Learning how to prepare and cook one new recipe a week will get you to nourishing traditional foods in less than a year. All these steps will help improve your family’s health, especially if you cut out all the processed industrial food.
The Big Changes
1. Buy meat, fish and fowl by the whole animal. Don’t buy meat, fish or fowl by the piece at the grocery store. These animals and fish are likely from confinement operations. Find a local source of pastured meat, wild fish, and fowl. Look for wild fish in season and purchase the whole fish. Make sure the animal or fowl has been on pasture its whole life and not in a feedlot or confined. Buy the whole animal and get a full service butcher to cut and wrap the meat into sizes suitable for your family. Get the butcher to give you everything, including parts you do not know how to cook yet. You will need to have a deep freezer to store your meat, fish and fowl. Pastured beef is the best value per pound.
2. Use organic butter, pastured lard and grease. Don’t buy margarine and shortening, even if it is organic. These products may be cheaper but you will pay with your health. If money is an issue use more pastured lard than butter. If you really want to save money, start a grease bucket and save the congealed fat from cooked beef, pork and fowl. You really get something for nothing. Grease is great for high heat cooking and frying. If you are thinking, “What, you want me to eat saturated fat! Are you mad? Haven’t you heard, saturated fat causes heart disease?” Please read Cholesterol: Friend or Foe.
3. Eat pastured eggs. Don’t buy eggs produced in a confinement operation. These eggs are of poor quality, being produced by heavily medicated hens under very stressful conditions. Find a local source of eggs where the hens are allowed freedom to eat bugs, worms and grass. Properly produced eggs are a nourishing, low-cost alternative to meat. Eggs are a great way to start the day and hard-boiled eggs make a great snack.
4. Eat organic or pastured raw cheese and homemade high-fat yoghurt. Try fermenting some foods. Don’t buy pasteurized cheese or commercial low-fat yoghurt. These are ersatz foods and are a shadow of the real thing. Making your yoghurt at home will save money and will enhance digestion. Homemade yoghurt with some frozen seasonal berries makes a delicious snack or dessert. Find a source of local raw cheese. Eating raw cheese is an easy, nutritious snack or addition to a meal. Try making your own fermented foods. It is easy and will save money. Here are some more recipes for fermented foods: dill pickles, kimchi, green tomatoes, horseradish, mustard and live whey culture.
5. Eat vegetables and fruit in season and from a local source. Don’t buy exotic fruits and vegetables out of season. These foods have been shipped halfway around the world and may come from questionable sources. The best part of fruits and vegetables, the phytochemicals, will be mostly lost after such a long journey. Buy local, certified organic or from a producer that follows organic principles. Go to your local farmer’s market and get to know your local producers. Find out if there is a Community Supported Agriculture CSA program in your area. Many of the cheapest vegetables are the most nourishing. Eat plenty of potatoes, broccoli, chard, celery, beets, kale, cabbage, carrots, mushrooms, zucchini, onions, garlic, squash, and lettuce. Grow a few pots of fresh herbs for low-cost garnishing on salads. While in season, consider buying vegetables and fruit in bulk and store for the winter.
6. Buy organic dried foods in bulk from a source you can trust. Don’t waste your money buying small packages of dried goods. You can save money by buying your organic grains, beans, legumes, dried fruits, herbs, and spices in bulk. You will need to find a dark, dry, and cool area of your house to store these foods. Try to buy this season’s harvest whenever possible.
7. Buy organic nuts and seeds in bulk from a source you can trust. Don’t waste your money buying small packages of nuts and seeds. Many of these packaged snacks are old and include numerous unhealthy additives. Try to buy this season’s harvest of nuts and seeds whenever possible. Nuts and seeds store best in the shell but most nuts and seeds are now sold shelled and need to be stored in a freezer. Try to buy this season’s harvest whenever possible to avoid stale products.
8. Put your money into whole foods rather than supplements. Don’t buy that low-cost multi-vitamin found in the drug store. There are many excellent supplements, such as fermented cod liver oil or probiotics, but if your budget is limited, use your money on real food first. Supplements are by their very nature highly processed, thus you will pay more for less. As your diet becomes more nutrient dense, your need for supplements will be reduced. Spend some time learning about superfoods before wasting money on supplements.
9. Eat offal from a pastured animal. Don’t supplement, eat offal! Liver, kidneys, heart, sweetbreads and brains are superfoods. If you are thinking about taking supplements, eat offal first. Offal was prized by most traditional cultures and are a rich source of nutrients.
The Little Changes
10. Make your own salad dressing. Don’t buy bottled salad dressing that is full of rancid vegetable oils, trans fats, and numerous unhealthy additives. For the cost of an average bottle of salad dressing you can make your own from the finest organic ingredients. Once you learn how to make your own dressing it takes a few minutes each week. Here is a recipe for Mustard Seed Dressing, Orange Ginger Dressing and Caesar Dressing. These are three family favorites.
11. Make a large bowl of seasonal mixed greens and vegetables and keep in the fridge for easy salads. Don’t waste your money on pre-mixed salad greens with packages of dressings with unhealthy ingredients. It takes a few minutes twice a week to have a fresh seasonal salad with each meal. Add your homemade salad dressing to the mixed greens just before eating.
12. Make your own bone broth once a week and use in soups, stews or reduction sauces. Don’t buy tetra packs of commercial stock. Don’t use processed bouillon cubes, even organic, which are made from very questionable ingredients. Bone broth is rich in minerals and helps in protein digestion. The congealed fat from bone broth can be used in cooking, which will save money. If you do not know how to make a homemade soups or stews, it is time to learn. Bone broth will make every soup or stew delicious. If you are lost in the kitchen read Nourishing Traditions by Sally Fallon. You can find a copy in the Kamloops Public Library.
13. If you eat grains, beans, and legumes, enjoy them whole with your meals. Don’t buy expensive prepackaged, or canned foods. These foods may be convenient but they do not have the nutrition found in home prepared grains, beans and legumes. Soak overnight and cook the next day. If you are wondering why you need to soak grains read Be Kind to Your Grains. If you are short on time, make a big pot once a week and store the cooked grains, beans and legumes in the fridge for later use. Use cold or re-heat as needed.
14. If you eat grains, make your our breakfast cereal. Don’t buy boxed cold breakfast cereal, even if it is made from organic whole grains. These processed foods are very expensive, difficult to digest, and poor in nutrition. Even the most expensive organic grains will be far cheaper than these heavily processed breakfast cereals. Make your own breakfast cereal with organic whole grains that are soaked overnight before cooking. If you are short on time, make a big pot once and week and store the cooked cereal in the fridge for later use. Heat up a small amount of the cooked cereal in the morning for breakfast. Remember to top with lots of raw cream or butter to help your body utilize the nutrients in the cereal and slow down your insulin response.
15. Make healthy homemade cookies and have frozen fruit for quick snacks. Don’t buy expensive cookies and cake with questionable ingredients. Have some frozen fruit for quick snacks and everyday desserts. Don’t buy those expensive little packages of organic berries from the grocery store. In season, find a local source of organic berries and freeze a year’s supply. Here are some recipes for cookies and cakes: Lemon Coconut Cookies, Chocolate Brownies, Butter Tart Squares, Coconut Almond Bark and Nanaimo Bars. Use these sweet desserts for special occasions.
16. If you eat grains, make healthy homemade bread and crackers. Don’t buy breads and crackers made with rancid flour, rancid vegetable oils, trans fats, and numerous unhealthy additives. The staff-of-life has become a shadow of its former greatness. Grind your own flour from organic whole grains and grow your own sour dough culture. Making bread can be made easier by making bread once a week or by storing a week’s worth of dough in the fridge and bring out a loaves’ worth in the morning before baking. If grinding your own flour is not possible, try sprouting the grain for three days and use a food processor to make a dough from the sprouted grain. For more information about the staff-of-life and the staff-of-death please read Dirty Secrets.
18. If possible, grow your own garden. Don’t worry if all you have is a small patio or windowsill. Start with a small herb garden for parsley, cilantro, thyme, oregano, sage, rosemary and other favorite herbs. Use these fresh herbs on your daily salads. Grow a few tomato plants or peas in pots. It is very satisfying to grow your own food.
19. If you are inclined, get a few hens for fresh eggs and meat. If you have the space consider getting a miniature goat or cow for raw milk. Lobby your government for changes in regulations to promote local food security. Hens will produce eggs and improve your garden fertility. Getting a source of high quality raw dairy is worth the trouble. Raw dairy is one of the most delicious, nourishing foods. Lobby your local, provincial, and federal governments to change laws so we can all can grow healthy food on our properties. This will increase food security for everyone.
20. Invest in your long-term health. Don’t skimp on your food budget. Economize by eating at home and save on meals out. If you are looking for nourishing recipes please see Specific Carbohydrate Diet (SCD): Recipes which is an index of all the recipes on this website. Cut out all the junk food, even the organic junk food, and use this money to buy high quality whole foods. Eating whole foods will keep you healthy and avoid loses in wages due to sick-time off work. It might even spare your life, by avoiding some dreaded disease. Look through the WAPF Shopping Guide for tips on assessing the quality of your food choices. If you haven’t read 25 Step to Nourishing Traditional Foods, please do so. If you are a visual learner please watch the Wise Tradition Beginner Video Series.